BrainShift
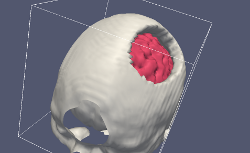
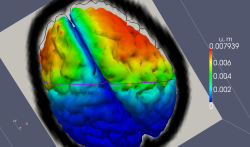
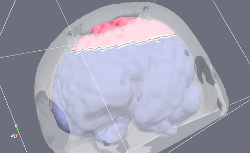
In this project we developed an effective numerical simulation of the brain shift process during a craniotomy procedure for robot-assisted awake neurosurgery. Despite the fact that it incorporates many physical effects into the underlying mathematical model, operates on a large simulation domain with high resolution - it is 100 times faster than the real time even if deployed on a regular laptop. This remarkable performance enabled us to determine unknown patient and operation specific model parameters intra-operatively "on the fly" through iterative smart guessing and subsequent calibration of the intermediate results with the stereo camera observations. This way a full picture of brain deformation was generated, which is otherwise not available to the surgeon through direct examination by means of ultra sound, video cameras or MRI. This synthesized information, as common in image guided surgery, is used by the robot and/or physician for navigation, operative planning and identifying the target location. BrainShift application is part of the cognitive and diagnostics module of the robot developed within the framework of the ACTIVE project.
About ACTIVE project
The ACTIVE exploits ICT and other engineering methods and technologies for the design and development of an integrated multi-robotic platform for neurosurgery. A light and agile redundant robotic cell with 20 degrees-of-freedom (DoFs) and an advanced processing unit for pre- and intra-operative control will operate both autonomously and cooperatively with surgical staff on the brain. As the patient will not be considered rigidly fixed to the operating table and/or to the robot, the system will push the boundaries of the state of the art in the fields of robotics and control for the accuracy and bandwidth required by the challenging and complex surgical scenario.