Focus
This simulation application has been developed to facilitate R&D and deployment of a microfluidic device for separating mixtures of proteins (hereinafter the word "protein" refers to protein as well as to peptide). The separation process is based on electrical manipulation of protein's ambient pH. This endeavour was undertaken jointly by Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. and Technion - Israel Institute of Technology.
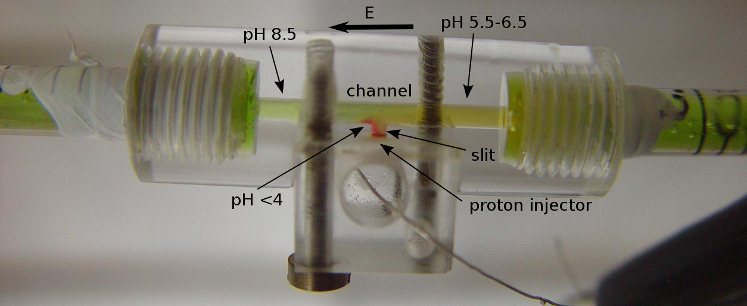
The device comprises a confined separation channel (36-90mm x 1-3mm x 0.5-0.15mm), means of generating a longitudinal electric field traversing the channel, a proper electrolyte solution, means (based on bipolar membrane (BPM) and ion exchange membrane (IEM) technologies) for injecting protons and/or hydroxyl ions at specific points along the separation channel in a controlled way, and means for introducing protein mixture.
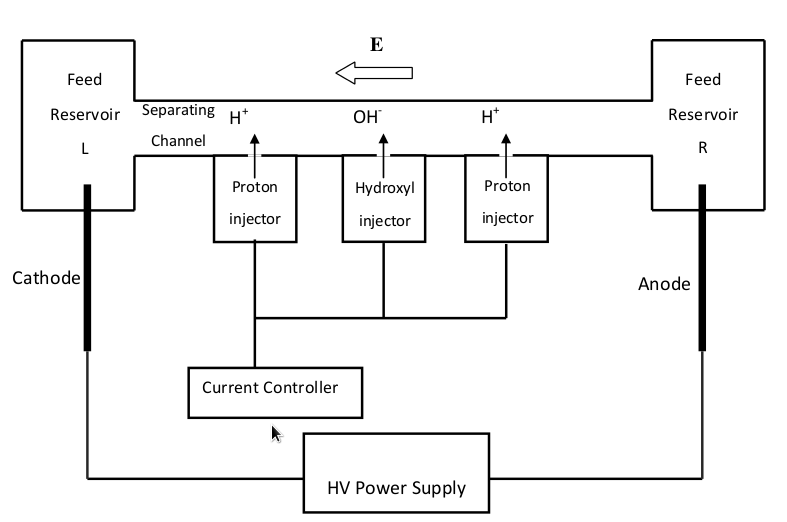
When operating the system, protein mixture is first inserted to the channel. Then, the longitudinal high voltage is turned on together with the ion injectors. The latter operate with either constant currents or temporally dependent ones, according to the separation strategies developed using Focus application. The resulting conditions in the channel lead to protein focusing and separation.
The R&D team was assigned two tasks: optimization of the injectors positions and development of the separation strategies. Achieving both goals required deep understanding of tendencies and processes taking place in the device during the focusing and separation procedure. Experimental observations and measurements of these processes are rather complicated and provide only limited insight. Therefore it was decided to create a computer model of the system. However due to inability of the standard software products to deliver necessary information, a custom simulation had to be designed. This mission was delegated to Avtech Scientific. Some of the features and requirements are listed below; all of them were implemented in the Focus application:
- Stable and reliable work for a wide range of input parameters
- Absence of non-physical parameters, so no background knowledge in numerical simulations is required from end users
- High spatial and temporal resolution on one hand and large system size and long simulated intervals of time on the other
- Effortless geometry manipulations with fully automatic mesh generation
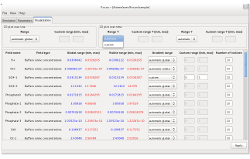
- The program should be able to deal with different buffer mixtures and several proteins (typically 4 buffers and 2 proteins which means 15 components) with corresponding protonization reactions
- Reasonable computation time
- Intuitive and informative Graphical User Interface (GUI) capable to visualize and process big amounts of data (typically several GBytes)
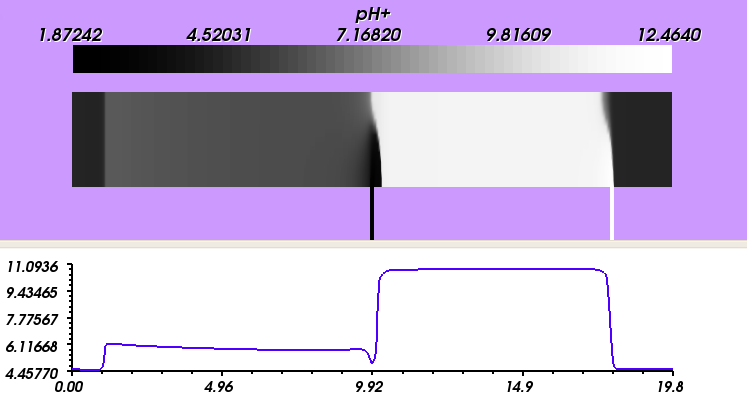
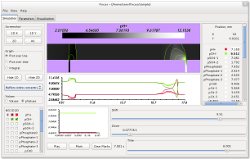
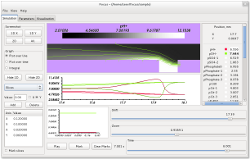
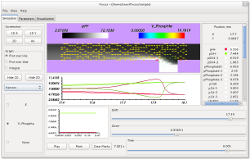
The pictures below depict a course of separation process predicted using Focus application (squeezed in its length in order to provide overview of the whole system) and the subsequent implementation of the computed separation strategy in an experiment.